Towards Human-Level Bimanual Dexterous Manipulation with Reinforcement Learning —— Yuanpei Chen, Yaodong Yang, et al.
作者在不同难度的 handover 任务上分别使用 PPO 和 MAPPO 进行了对比实验,结果显示在大部分的任务上,PPO 的表现优于 MAPPO。但是,任务越困难、越需要双手合作时,PPO 和 MAPPO 之间的性能差异越小。当任务非常困难时,MAPPO 的效果超过了PPO,这表明多智能体算法可以提高双手合作操作的性能。
Dynamic Handover: Throw and Catch with Bimanual Hands —— Yuanpei Chen, et al.
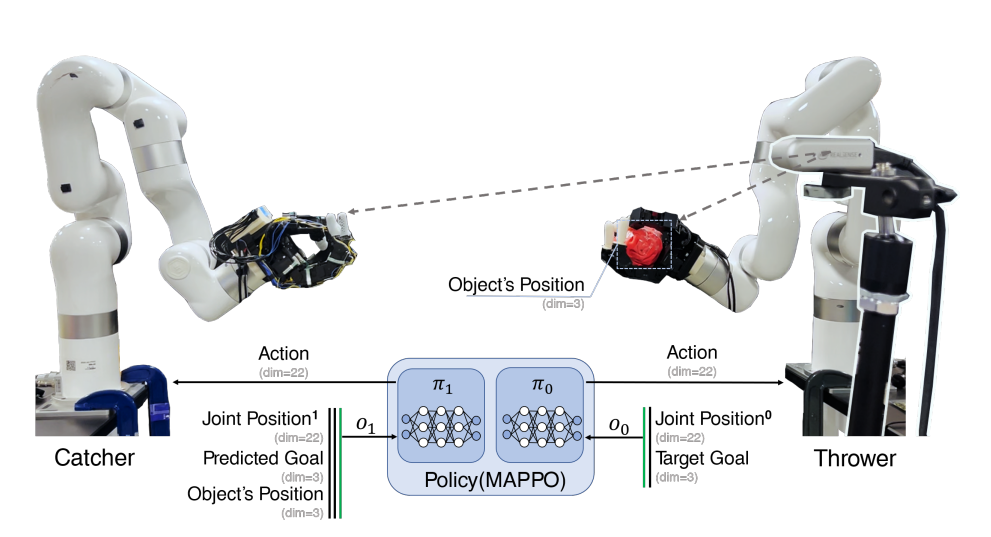
- 通常情况下,Single-Agent 比 Multi-Agent 更容易训练,因为 SA 设置下 thrower 和 catcher 可以互相访问两者的状态。但实验结果显示 MA 的表现更好,原因是 SA 接受了更多的信息, 会更容易在环境中发生过拟合, 导致泛化能力没有 MA 强.
- MARL 能有效减少 sim2real 的 gap, 因为每个智能体使用了局部观测来改进每个策略的鲁棒性.
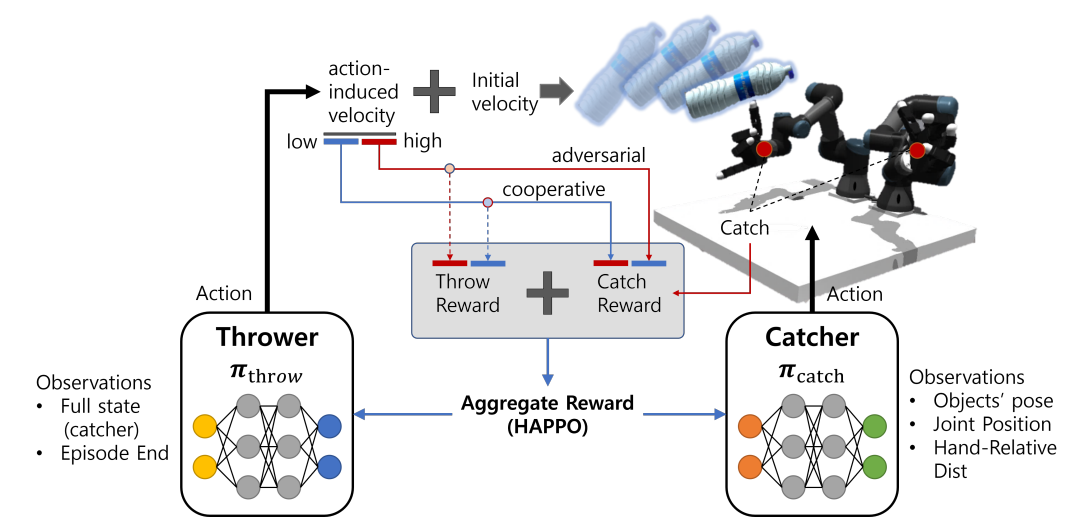
Learning Dexterous Bimanual Catch Skills through Adversarial-Cooperative Heterogeneous-Agent Reinforcement Learning —— Taewoo Kim, Youngwoo Yoon, and Jaehong Kim
DexCatch: Learning to Catch Arbitrary Objects with Dexterous Hands —— Fengbo Lan, Shengjie Wang, et al.
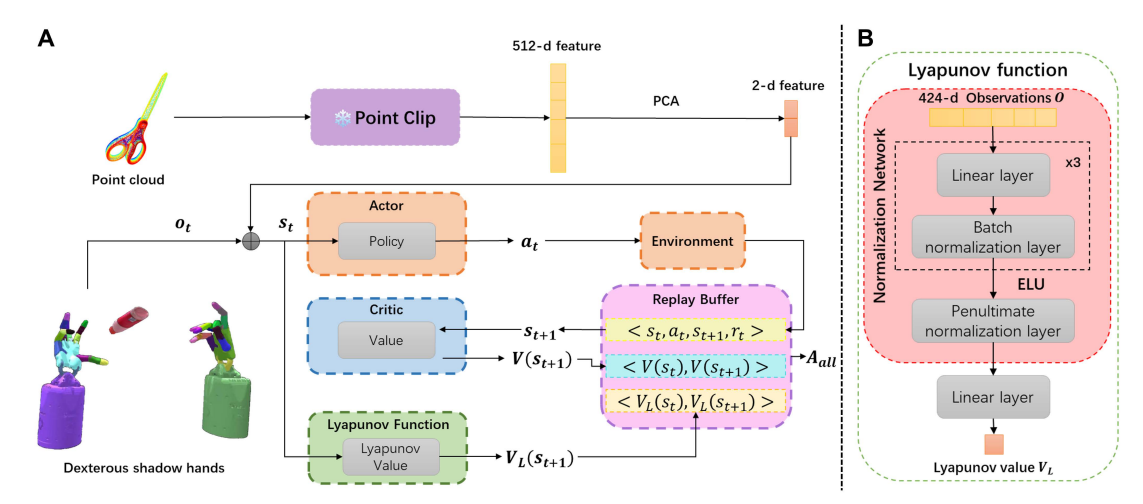
the basic PPO algorithm encounters two key challenges: How to achieve efficient throwing and stable catching without falling? We make some algorithmic modifications to the basic PPO algorithm. First, to accelerate the learning of throwing, we design an intrinsic advan4 tage and add penultimate normalization layers in the network. Secondly, a stable catching behaviour is holding the object in the palm without falling the object. As depicted in Fig. 3, the maximum sum reward (optimality) can not guarantee the generation of the stable catching behaviour. To encourage more stable catching, we include the Lyapunov stability condition in policy learning.
